How ya'll
doing?Sorry.. I forgot to introduce what is our topic about because of my
passion typing up till I forgot to introduce the subject. For your information,
this time we will learn more about what is parallel processing. I'm sure many
of you still do not understand about what is parallel processing. Okay, today
I'm very happy to talk about what is parallel processing..Let’s get started...
Do You Know That??
Let’s start with what is Parallel Processing
Parallel Processing is an asynchronous communication may be further
classified as serial and parallel, depending upon number of bits being
transferred at the same instant. In serial communication, only one bit of
information is transferred at a time, while in parallel communication, multiple
bits, generally 8 or 12 or 16, are transferred at the same time. Therefore, the
requirement of number of transmission lines necessary to connect two
communicating devices would be less for serial communication than that is
required for parallel communication. However, the speed of data transfer would
be faster in case of parallel communication than the speed of serial communication.
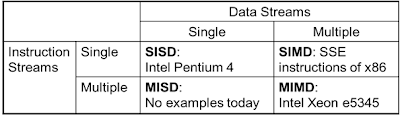
Single Instruction, Single Data
Stream -SISD
uni-processor
single processor
single instruction stream
data stored in single memory
Single
Instruction, Multiple Data Stream – SIMD
• Single
machine instruction
Each
instruction executed on different set of data by different processors
Number
of processing elements
Machine
controls simultaneous execution
–
Lockstep
basis
Each processing element has associated data
memory
• Application: Vector and array processing
Multiple
Instruction, Single Data Stream - MISD
· Sequence of data
· Transmitted to set of processors
· Each processor executes
::Not
clear if it has ever been implemented different instruction sequence :)
Multiple Instruction, Multiple Data Stream- MIMD
- Set of processors
- Simultaneously executes different instruction
sequences
- Different sets of data
Examples:
SMPs, NUMA systems, and Clusters
The advantages of Block Diagram of Tightly Coupled
Multiprocessor are the processors share memory and also we can
communicate via that shared memory.
Next we move on to Symmetric Multiprocessor Organization. What is
Symmetric Multiprocessor Organization? For those who didn’t know what it
really is. Actually it involves a multiprocessor computer
hardware architecture where two or more identical processors are connected to a
single shared main memory and are controlled by a single OS instance. Most
common multiprocessor systems today use an SMP architecture. In the case of
multi-core processors, the SMP architecture applies to the cores, treating them
as separate processors.
Symmetric Multiprocessor Organization or SMP systems are tightly coupled multiprocessor
systems. For your information, the processors running independently, each
processor executing different programs and working on different data and with
capability of sharing common resources such as memory, I/O device, interrupt
system and etc and connected using a system bus or a crossbar.
The advantages of SMP:
-Performance
-If some work can be done in parallel
-Availability
-Since all processors can perform the same
functions,failure of a single processor does not halt
the system
-User can
enhance performance by adding additional processors
Scaling
-Suppliers can offer range of products based on number
of processors
Multiprocessor Architectures:
Distributed Memory :)
Do you know what is the benefit of cluster???
It is absolute scalability, incremental
scalability, high availability and last but not least it
is superior price (performance).
Here is cluster configuration:
Clusters
|
Symmetric
Multiprocessor Organization (SMP)
|
Easier to manage and control
|
Superior incremental & absolute scalability
|
Closer to single processor systems
Ø Scheduling is main difference
Ø Less physical space
Ø Lower power consumption
|
Less cost & Superior availability in redundancy
|
Similarities
|
between
|
Clusters
|
and
|
SMP
|
Both provide multiprocessor
support to high demand applications
|
Both available commercially
|
Non-uniform Memory Access
(NUMA)- (Tightly coupled)
• Alternative to SMP & Clusters
• Non-uniform memory access
• All processors have access to all parts of memory
• Using load & store
• Access time of processor differs depending on region
of memory
• Different processors access different regions of
memory at different speeds
Cache coherent NUMA ?
Cache coherence is maintained
among the caches of the various processors
Significantly different from SMP and Clusters
Parallel
Programming
·
Parallel software is the problem
·
Need to get significant performance improvement
· Otherwise,
just use a faster uniprocessor, since it’s easier!
Difficulties:
·
Partionong
·
Coordination
·
Communications overhead
Definitions
of Threads and Processes
• - Threads in
multithreaded processors may or may not be same as software threads
• Process:
= An instance of program running on computer
• Thread:
dispatchable unit of work within process
= Includes
processor context (which includes the program counter and stack pointer) and
data area for stack
=Thread
executes sequentially
Interruptible:
processor can turn to another thread
• Thread switch
Switching
processor between threads within same process
Typically
less costly than process switch
Parallel, Simultaneous
Execution of Multiple Threads
Execution of Multiple Threads
• Simultaneous
multithreading
Issue
multiple instructions at a time
One thread
may fill all horizontal slots
Instructions
from two or more threads may be issued
With enough
threads, can issue maximum number of instructions on each cycle
• Chip
multiprocessor
Multiple
processors
Each has
two-issue superscalar processor
Each
processor is assigned thread
Can issue up
to two instructions per cycle per thread
Interconnection
Networks
Network
topologies
◦ Arrangements
of processors, switches, and links
NETWORK CHARACTERISTICS
Performance
◦ Latency per
message (unloaded network)
◦ Throughput
– Link
bandwidth
– Total network
bandwidth
– Bisection
bandwidth
◦ Congestion
delays (depending on traffic)
Cost
Power
Routability in silicon
Multicore Processor
multi-core processors
combining two or more independent cores into a single package have become
increasingly popular within the personal computers market (primarily from Intel
and AMD) and game consoles market (e.g. the eight-core Cell processor in the
Sony PS3 and the three-core Xenon processor in the Xbox 360). However, despite
the significant potential that is offered by these processing structures,
parallel systems often pose many unique development challenges that simply did
not exist when developing products for single processor platforms. In fact, the
amount of performance that is gained by the use of multi-core processors is
frequently highly dependent not only on the adopted parallel description of the
considered software structures, but also on several restrictions imposed by the
actual hardware architecture (e.g.: cache coherency, system interconnect, and
so on.
That’s all
for now..hope you guys more understand the topics this time of parallel
processing. Till we meet again in the next entry with much exciting topics...
Will share more about what is interesting topics
in my future posts! Toodles!NUR IYLIA ZUBIR
B031210032









thank you very much for this information and I hope you can explain more about the parallel processing architechture esp in SMPs,clusters and NUMA...
ReplyDeletewarm regards,
MIE@upm.xD
so much informative....its really helpful for us! Thank you.
ReplyDelete